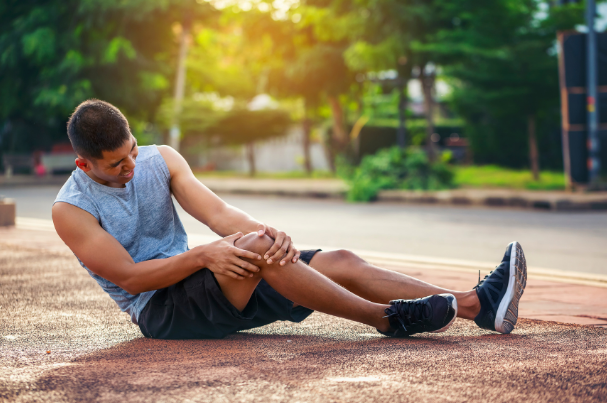

Magnesium Deficiency Symptoms: Understanding the Signs and Solutions
Magnesium is a vital mineral that supports numerous functions in the body, from muscle and nerve health to energy production and blood sugar regulation. However, when magnesium levels drop below the recommended range, it can lead to magnesium deficiency, manifesting through various symptoms that can disrupt daily life and overall health.
Common Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
Recognizing the symptoms of magnesium deficiency is crucial for early intervention. Here are the most common signs to watch for:
- Fatigue and Weakness
Magnesium plays a central role in energy production. A deficiency can result in a lack of energy, leaving you feeling drained and unable to perform daily tasks. Chronic fatigue, paired with weakness in muscles, is often a telltale sign. Learn more about how magnesium impacts energy in our guide on Magnesium for Energy Production. - Muscle Spasms and Cramps
One of the most noticeable symptoms of low magnesium levels is frequent muscle spasms or cramps. These involuntary contractions are not only painful but also disrupt physical activities. For insights into how magnesium supports muscle health, explore Magnesium 400® & B-Complex. - Abnormal Heart Rhythms
A magnesium deficiency can affect heart health by causing irregular heartbeats or palpitations. This is because magnesium regulates calcium and potassium, essential minerals for maintaining a steady heart rhythm. For more on magnesium’s cardiovascular benefits, see Benefits of Magnesium Supplements. - Nausea and Reduced Appetite
Digestive issues, such as a loss of appetite or unexplained nausea, may indicate magnesium deficiency. These early signs often go unnoticed but should prompt dietary adjustments or supplementation. - Nervous System Symptoms
Low magnesium levels can contribute to nervous system issues, such as irritability, difficulty concentrating, and even increased stress or anxiety. A great way to support both nerve and mental health is through products like MAGNESIUM 400®.
Causes of Magnesium Deficiency
Several factors can contribute to magnesium deficiency:
- Dietary Gaps: A diet lacking in magnesium-rich foods like nuts, seeds, and leafy greens.
- Health Conditions: Conditions like Crohn’s disease or type 2 diabetes can impair magnesium absorption.
- Medications: Long-term use of diuretics or antacids can deplete magnesium levels.
- Stress: Chronic stress can exacerbate magnesium loss from the body.
If you suspect your diet may lack magnesium, check out our list of Foods High in Magnesium.
Preventing Magnesium Deficiency
Prevention starts with understanding and addressing the root causes. Here are practical tips to maintain healthy magnesium levels:
- Dietary Adjustments
Incorporate magnesium-rich foods such as almonds, spinach, and whole grains into your meals. For a quick nutritional boost, consider adding VITACED B-Complex to your routine. - Supplementation
When dietary intake isn’t enough, supplements like MAGNESIUM 400® provide an easy solution. These supplements ensure you’re meeting your body’s magnesium needs. - Hydration and Exercise
Staying hydrated and engaging in regular physical activity can improve magnesium absorption and overall health. If cramps are an issue, Magnesium 400® & B-Complex is a great choice for muscle recovery.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While magnesium deficiency is often manageable through diet and supplementation, severe cases may require professional intervention. Symptoms like persistent muscle cramps, arrhythmias, or neurological issues warrant consultation with a healthcare provider.
In such cases, intravenous magnesium treatments might be necessary. To understand the broader impact of magnesium on overall health, visit VITACED B-Shot.
Conclusion
Magnesium is a cornerstone of health, and its deficiency can lead to a cascade of symptoms that affect your physical and mental well-being. Recognizing the early signs—such as fatigue, cramps, and heart irregularities—and taking proactive steps to address them is essential.
With solutions like MAGNESIUM 400® & B-Complex and dietary adjustments, maintaining optimal magnesium levels is achievable. Explore our comprehensive guide on magnesium benefits to take charge of your health today.


 United States
United States Germany
Germany